What is Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Elbow?
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is an irregularity of the bone surface within the elbow of young people (12-16 years). The irregularity is a fragment of bone and/or cartilage that has come away from the main surface of the humerus (bone of the upper arm). This fragment can still be attached to the body of the bone or can be loose within the elbow joint (see Figure 3).9 The bone fragment is similar to an island breaking off from the mainland.
OCD of the elbow joint is usually found in an area of the humerus called the capitellum. This area is within the joint in the outer half of the elbow from the body. This can be seen in Figure 1.
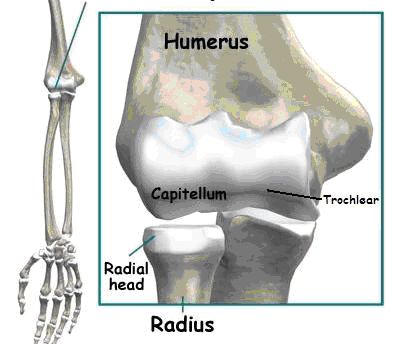 Figure 1: Locations of OCD of the Elbow. | 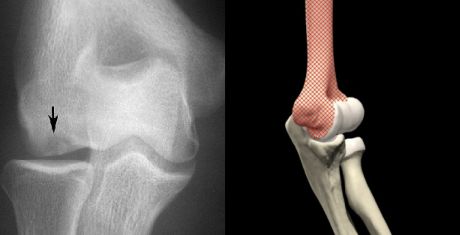 Figure 2: X-ray of OCD of the elbow (left) and side view of elbow joint (right). |
Table 1: Classsification of OCD
|
Classification |
Definition |
Description |
|
Stage I |
Stable bone fragment |
The bone fragment is still firmly attached, but there is a decreased blood supply to the bone and cartilage, with associated cartilage damage. Found in early OCD and not easily identified on an x-ray |
|
Stage II |
Loose bone fragment that is still attached to the main body of the bone |
The bone fragment is more defined (can be seen on an x-ray) and can move slightly. The fragment is still attached in its normal position on the humerus |
|
Stage III |
Loose bone fragment in joint |
This is the chronic stage where the bone fragment has separated from the humerus and is within the elbow joint (loose body). This can be seen easily on an x-ray and requires more invasive treatment |
|
Stage IV |
Radial head OCD |
The presence of a loose body in the elbow joint causes damage to the head of the radius (a bone of the forearm). This type of injury is very rare |
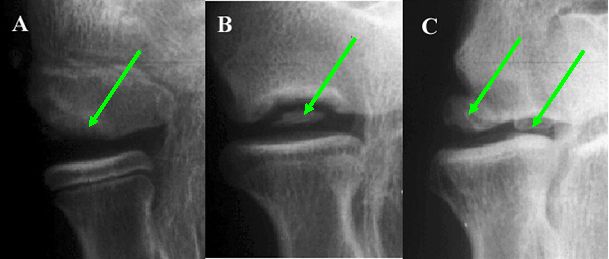
Figure 3: A) Attached fragment. B) Semi-attached fragment. C) Two unattached (displaced) fragments, also know as loose bodies.
Other areas less commonly associated with OCD of the elbow include the radial head (thumb-side forearm bone within the joint) and the trochlear (inner half of the joint from the body).4,11 These can also be seen in Figure 1. This condition can be seen in adults however this is quite rare.